Which Best Describes a Field Effect Transistor
FETs are devices with three terminals. Most commonly two types of FETs are available.

Understanding The Differences Between The N Channel And P Channel Field Effect Transistors Fets Technical Articles
All of the above.

. The FET transistor field-effect transistor controls the form and thus the conductivity of the charge carrier in a semiconductor through an electric field. Which best describes a field-effect transistor. A JFET can be used as a voltage-controlled resistor.
TCO 1 Which best describes a field-effect transistor. As they undergo an operation of a single-carrier type these FET transistors are also called unipolar transistors. 2 It is the oldest direct conversion technology with limited use today.
The name itself gives a brief idea about its working principle field effect these two words clearly indicates it is a transistor controlled by electric field. It is a three terminal unipolar device in which conduction is manipulated with the help of applied electric field. FET is an acronym used for field effect transistor.
3 It is the oldest indirect conversion technology that is no longer used in medical imaging. Maximum current for any JFET IDSS occurs when VGS 0 V. Field-effect transistors also known as unipolar transistors use either electrons or holes for the transport of electricity.
Since this transistor depends on an electric field its known as a Field Effect transistor. 5 A unipolar device in which the voltage at the gate controls the drain current A bipolar device attributed to having high input impedance A unipolar device in which current at the gate controls the collector voltage A bipolard device in which voltage at the gate controls the gate current. It is also a three-terminal element.
The metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor MOSFET is a FET whose gate is insulated from the main body of the transistor by a layer of metal oxide semiconductor such as SiO 2. The three terminals are similar to the transistors base emitter and collector but they are called the gate source and drain. Which best describes a field-effect transistor.
Called a Field-Effect TransistorFET. This layer is very thin and for this reason MOSFETs are prone to get damaged easily if they are subject to voltages higher than their ratings. A cluster of field-effect transistor.
Which statement best describes a charge-coupled device CCD. Field oxide Source metal Poly gate Drain metal n n b ˇ ˇ ˇ ˆ ˇ p-type Gate G Substrate or body B Source S Drain D n n L S D p Electron inversion layer G SD a b c ˇ. Field-effect transistors based on band-to-band tunneling TFETs have recently attracted a great deal of interest.
A current-controlled device in which current at the base controls the collector voltage A voltage-controlled device in which voltage at the gate controls the drain current A current-controlled device in which the current at the gate controls collector current A voltage-controlled device attributed to having. FET is three-terminal semiconductor devices with source drain and gate. FET sometimes is called unipolar transistor as it involves single carrier type operation.
C a voltage-controlled device in which voltage at the gate controls current through the dev D a current-controlled device in which the current at the gate. The initial FETs we will use the 2N5485 have identical packages to the transistors we used in earlier in the semester. Its operation is based on a controlled input voltage.
Field Effect Transistor FET Definition. Field-Effect Transistors FETs have much higher input impedance than do bipolar junction transistors BJTs and would therefore seem to be ideal devices for op amp input stages. The transistor has amplified the original signal.
A Field Effect Transistor FET is a three-terminal semiconductor device. However BJT is a current controlled device and JFET is controlled by input voltage. High input impedance is an important characteristic of FET.
Most of todays transistors are MOS-FETs or Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors. However they cannot be manufactured on all bipolar IC processes and when a process does allow their manufacture they often have their own problems. 1 Which best describes a Field-Effect transistor.
The field-effect transistor is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. Source gate and drain. Even more on the Field Effect Transistor.
The transistor is the basic component in semiconductor manufacturing in modern microchips there are found several millions to billions of transistors. A a current-controlled device in which current at the gate controls voltage at the drain B a voltage-controlled device with a low input impedance. A field-effect transistor or FET is a transistor where the output current is controlled by an electric field.
FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. The strong interest stems from the fact that TFETs potentially allow the realization of transistors with superior switching behavior compared to conventional metal-oxide semiconductor FETs and hence allow reducing the operational voltage as well as the off-state. By appearance JFET and bipolar transistors are very similar.
1 It is the oldest direct conversion technology that is still in use today. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since. All the forms of FET have high input impedance.
The basic types of FET transistors are completely different from BJT transistor basics.
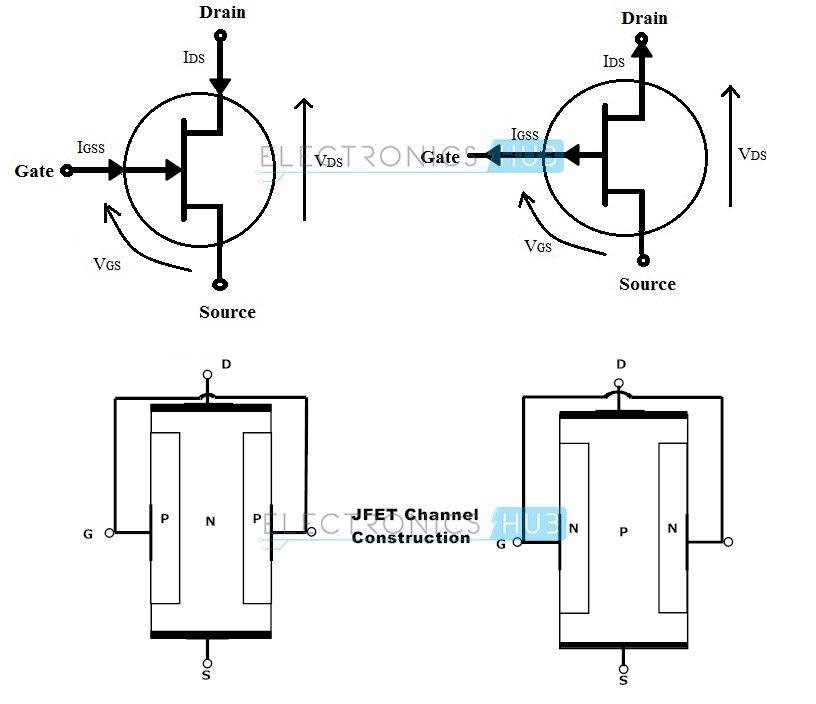
Junction Field Effect Transistor Jfet N Channel Jfet Biasing V I
Junction Field Effect Transistor Jfet N Channel Jfet Biasing V I

Ion Sensitivity From Current Hysteresis In Inas Nanowire Field Effect Transistors Functionalized With Ionophore Doped Fluorosilicone Membranes Sciencedirect

A Schematic Illustration Of The Field Effect Transistor Based On Download Scientific Diagram

Organic Field Effect Transistors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Junction Field Effect Transistor Or Jfet Tutorial

Junction Field Effect Transistor Or Jfet Tutorial

Junction Field Effect Transistor Or Jfet Tutorial
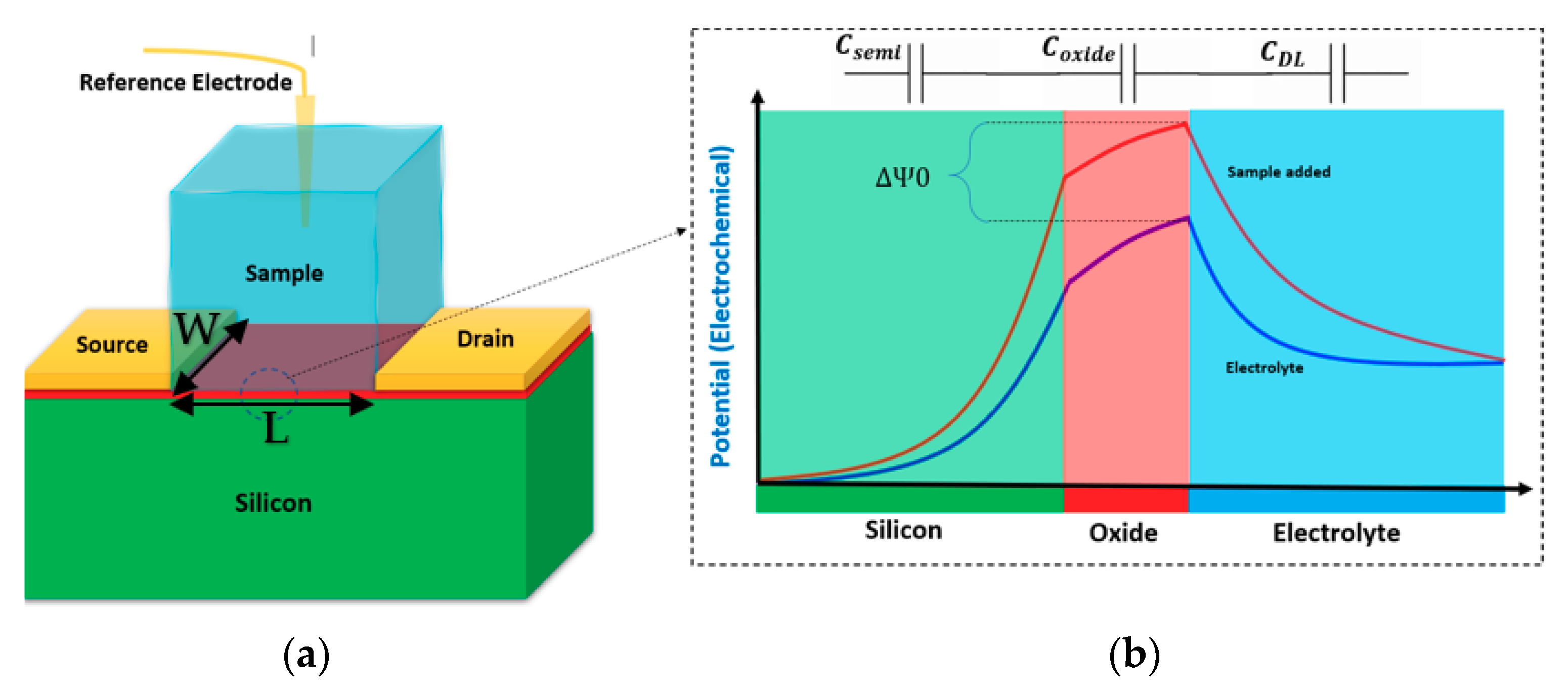
Biosensors Free Full Text Recent Advances Of Field Effect Transistor Technology For Infectious Diseases Html

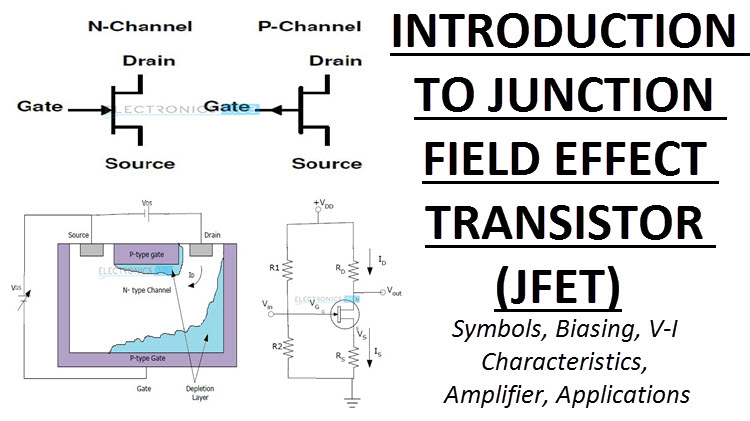
Understanding The Differences Between The N Channel And P Channel Field Effect Transistors Fets Technical Articles

Field Effect Transistors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Organic Field Effect Transistors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Si Nanowire Field Effect Transistor Structures Under Study Schematic Download Scientific Diagram

Junction Field Effect Transistor Or Jfet Tutorial
Field Effect Transistors Fets As Transducers In Electrochemical Sensors Re Study Hix Hix

Field Effect Transistors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Field Effect Transistors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Understanding The Differences Between The N Channel And P Channel Field Effect Transistors Fets Technical Articles

Comments
Post a Comment